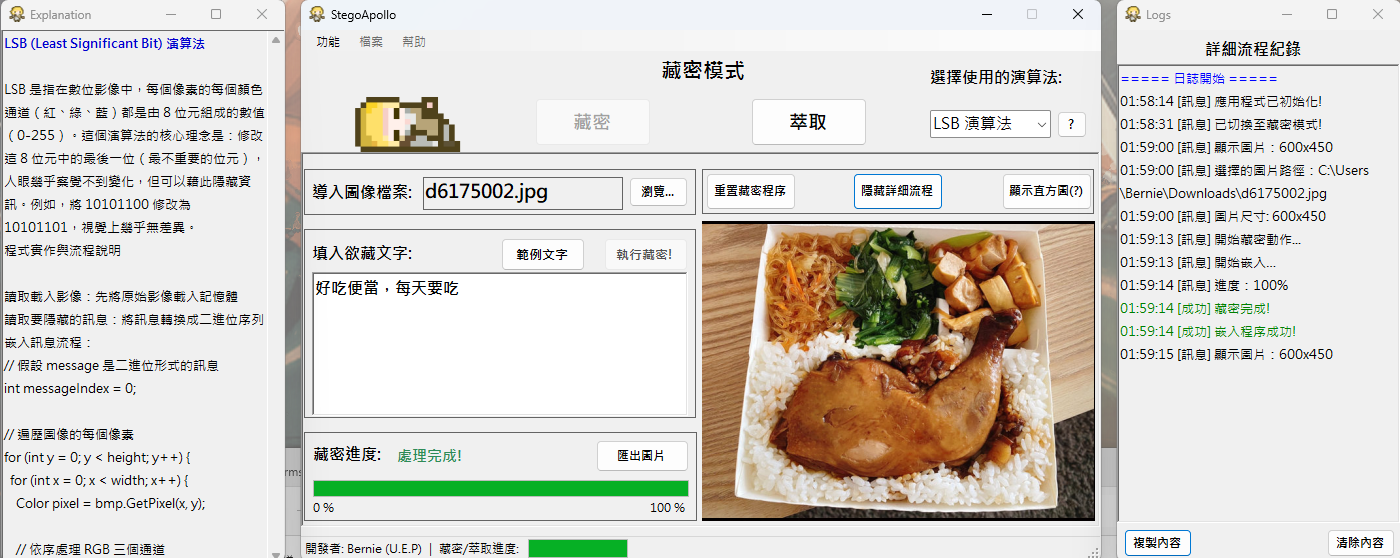
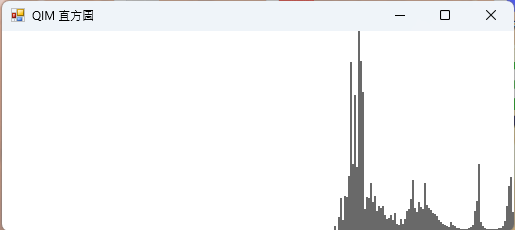
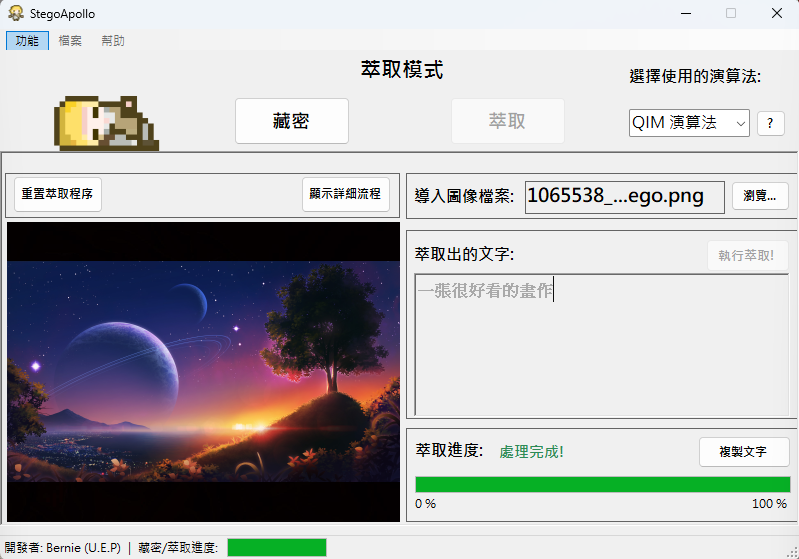
StegoApollo - Steganography Tool
A C# Windows Forms steganography application using MVP architecture, implementing four algorithms (LSB, QIM, DCT, Histogram Shift), featuring histogram visualization, real-time logging, and interactive algorithm explanation panels.
Project Introduction
StegoApollo is a Windows Forms Steganography Application providing a complete solution for embedding and extracting messages in images. The project implements four steganography algorithms (LSB, QIM, DCT, Histogram Shift), adopts an MVP (Model-View-Presenter) architecture design, and integrates histogram visualization, real-time logging, and algorithm explanation features. It is suitable for information security education and steganography research.
Core Concepts
- Multi-Algorithm Support: LSB (Least Significant Bit), QIM (Quantization Index Modulation), DCT (Discrete Cosine Transform), Histogram Shift
- Education-Oriented Design: Interactive algorithm explanation panel, real-time operation logs, histogram visualization
- Modular Architecture: Strategy Pattern design, separation of service and utility layers, extensible interface definition
- Professional UI/UX: Progress indicator, error handling mechanism, one-click export functionality
My Responsibilities
As the sole developer of the project, I am responsible for:
System Architecture Design
- Designed dual-project architecture: StegoLib (Class Library) + StegoApolloUI (WinForms App)
- Implemented Strategy Pattern: IStegoService interface + 4 algorithm implementations
- Established MVP architecture: MainForm (View) + MainPresenter (Presenter) + StegoLib (Model)
- Designed separation of service and utility layers: Services/ + Utilities/
Core Algorithm Implementation (StegoLib Class Library)
- LsbStegoService (148 lines): Least Significant Bit embedding and extraction
- Supports 1-2 bit embedding in RGB three channels
- 4-byte prefix for message length
- Unsafe Code pointer operations for performance optimization
- QimStegoService (194 lines): Quantization Index Modulation
- Grayscale channel quantization processing
- Adjustable Delta step size (default 8)
- Histogram generation support
- DctStegoService (210 lines): Discrete Cosine Transform
- Frequency domain embedding technique
- 8×8 block DCT transformation
- Mid-frequency coefficient modification
- HistShiftService (586 lines): Histogram Shift
- Reversible information hiding technique
- Peak/Zero point selection algorithm
- Complete histogram statistics and shift logic
Utility Library Development (Utilities/)
- ImageHelper (41 lines): Image loading, saving, format conversion
- HistogramHelper (46 lines): Grayscale histogram calculation and Bitmap generation
- DctUtils (52 lines): DCT and IDCT transformation functions
- LogManager (100 lines): Hierarchical logging system (Info, Warning, Error, Debug)
- MetadataHelper (79 lines): EXIF metadata reading and writing
UI Development (Windows Forms)
- MainForm (708 lines + 919 lines Designer):
- Image selection and preview
- Algorithm selection (ComboBox)
- Embed/Extract mode switching
- Progress bar visualization (ProgressBar)
- Result export functionality
- LogForm (109 lines + 107 lines Designer):
- Real-time log display (RichTextBox)
- Color coding (Info=Black, Warning=Orange, Error=Red)
- Auto-scroll to latest message
- ExplanationForm (27 lines + 59 lines Designer):
- LSB algorithm explanation
- QIM algorithm explanation
- Interactive panel switching
Core Features
1. LSB (Least Significant Bit) Steganography
- Embedding Algorithm:
- Convert message to UTF-8 bytes
- 4-byte prefix for length (supports up to 4GB messages)
- Traverse image pixels' R, G, B channels
- Replace lowest 1-2 bits per channel with message bits
- Capacity calculation:
width × height × 3 × bitsToUse
- Extraction Algorithm:
- Read first 4 bytes to get message length
- Extract lowest bits from RGB channels
- Reassemble into bytes and convert to UTF-8 string
- Features:
- Nearly invisible to human eyes (visual quality PSNR > 50dB)
- Large capacity (100KB image can embed ~37KB message)
- But weak resistance to interference (compression or filters can destroy)
2. QIM (Quantization Index Modulation) Steganography
- Embedding Algorithm:
- Convert image to grayscale
- Quantization step Delta (default 8)
- Message bit = 0 → quantize to even multiple
- Message bit = 1 → quantize to odd multiple
- Formula:
q = round(pixel / Δ),newPixel = q × Δ + (bit × Δ/2)
- Extraction Algorithm:
- Calculate quantization index
q = round(pixel / Δ) - Extract bit
bit = q % 2
- Calculate quantization index
- Features:
- Stronger resistance to compression (can extract after JPEG compression)
- Histogram visualization support
- Smaller capacity than LSB (single channel only)
3. DCT (Discrete Cosine Transform) Steganography
- Embedding Algorithm:
- Divide image into 8×8 blocks
- Perform 2D DCT transformation on each block
- Embed message in mid-frequency coefficients (avoid low and high frequencies)
- Perform IDCT inverse transformation
- Extraction Algorithm:
- Perform DCT on blocks
- Extract message from mid-frequency coefficients
- Features:
- Good JPEG compression resistance (frequency domain embedding)
- Excellent visual quality
- Higher implementation complexity
4. Histogram Shift Steganography
- Embedding Algorithm:
- Calculate grayscale histogram
- Select Peak point (highest frequency) and Zero point (frequency 0)
- Shift pixel values between Peak and Zero
- Embed message at Peak point (Peak+1 or maintain Peak)
- Extraction Algorithm:
- Identify Peak point
- Restore shifted pixels
- Completely lossless extraction
- Features:
- Reversible Steganography: Can perfectly restore original image after extraction
- Capacity limited by Peak point frequency
- Suitable for medical imaging and other scenarios requiring lossless restoration
5. Visualization and Logging System
- Histogram Generation:
- 256-level grayscale statistics
- Bitmap rendering (800×600)
- Supports QIM algorithm only
- Logging System:
- 4 levels: Info, Warning, Error, Debug
- Color-coded visualization
- Real-time scroll to latest message
- Records operation timestamps
- Algorithm Explanation:
- LSB principle explanation (bit replacement diagram)
- QIM principle explanation (quantization modulation formula)
- Interactive switching
Technologies Used
Development Framework
- .NET Framework 4.7.2: Target framework
- Windows Forms: GUI framework
- C# 7.3: Programming language
- System.Drawing: Core image processing library
Design Patterns
- Strategy Pattern: IStegoService interface + 4 algorithm implementations
- MVP Pattern: Model (StegoLib) + View (MainForm) + Presenter (MainPresenter)
- Factory Pattern: Algorithm service instantiation
- Singleton Pattern: LogManager global log management
Key Technologies
Unsafe Code: Allow unsafe code for performance optimization
<AllowUnsafeBlocks>true</AllowUnsafeBlocks>
Pointer Operations: Direct Bitmap memory access (BitmapData.Scan0)
Generics and Interfaces: IStegoService<T> algorithm abstraction
Event-Driven: IProgress<int> progress reporting
Development Tools
- Visual Studio 2019/2022: IDE
- Git: Version control
Project Status
Current Version: Feature Complete (develop branch)
- Project Structure: Dual-project solution (StegoLib + StegoApolloUI)
Feature Completion
- ✅ Completed:
- 4 steganography algorithms (LSB, QIM, DCT, Histogram Shift)
- Windows Forms graphical interface
- Complete embedding and extraction workflow
- Histogram visualization (QIM)
- Real-time logging system
- Algorithm explanation panel
- Progress indicator
- PNG format export
- Error handling mechanism
- 📋 To Be Improved:
- More visualization options (LSB channel separation)
- Error handling for unsupported image formats
- Unit test coverage
- UI/UX optimization
Development Challenges and Lessons
1. LSB Algorithm Implementation
Challenge: How to efficiently modify the lowest bits of pixels?
Solution:
- Used bitwise operations:
(value & ~mask) | (bit << position) - Clear target bit:
& ~(1 << b) - Set new bit:
| (payloadBit << b)
Lessons Learned:
- Deep understanding of bitwise operation techniques
- Mastered RGB color space operations
- Learned message length prefix encoding (4-byte header)
2. QIM Quantization Index Modulation
Challenge: How to implement robust embedding in grayscale channel?
Solution:
- Selection of quantization step Delta (8 is optimal balance)
- Even/odd quantization:
q % 2determines message bit - Formula derivation:
newPixel = round(pixel / Δ) × Δ + bit × Δ/2
Lessons Learned:
- Understood quantization theory and digital signal processing
- Mastered grayscale conversion techniques
- Learned anti-compression steganography design
3. Unsafe Code Performance Optimization
Challenge: SetPixel/GetPixel performance bottleneck (each call requires Marshal).
Solution:
- Used
LockBitsto lock Bitmap memory - Direct pixel array access via pointers
UnlockBitsunlock after batch processing
Performance Improvement:
- SetPixel/GetPixel: ~100-200 ms/pixel
- Unsafe Code: < 1 ms/pixel
- 100-200x improvement
Lessons Learned:
- Understood .NET memory management
- Mastered Unsafe Code best practices
- Learned performance analysis and optimization
4. Strategy Pattern Application
Challenge: How to design an extensible multi-algorithm architecture?
Solution:
Defined IStegoService interface:
public interface IStegoService { StegoResult Embed(Bitmap coverImage, string message, IProgress<int> progress = null); StegoResult Extract(Bitmap stegoImage, IProgress<int> progress = null); }Each algorithm independently implements the interface
UI layer calls through interface without knowing concrete implementation
Lessons Learned:
- Deep understanding of Strategy Pattern
- Mastered Dependency Inversion Principle (DIP)
- Learned interface-driven development
5. MVP Architecture Design
Challenge: How to separate UI logic from business logic?
Solution:
- Model (StegoLib): Core algorithms and data models
- View (MainForm): UI presentation and user interaction
- Presenter (MainPresenter): Coordinates View and Model, handles events
Lessons Learned:
- Understood difference between MVP and MVC
- Mastered UI and logic separation techniques
- Improved code testability
6. Histogram Visualization
Challenge: How to render 256-level grayscale statistics as a histogram?
Solution:
- Count pixels for each grayscale value (array
counts[256]) - Find maximum value as scaling reference
- Use Graphics.DrawLine to draw vertical bars
Lessons Learned:
- Mastered GDI+ drawing techniques
- Understood histogram statistics principles
- Learned data visualization design
Project Highlights
Technical Innovation
- ✅ Complete implementation of 4 steganography algorithms (LSB, QIM, DCT, Histogram Shift)
- ✅ Unsafe Code performance optimization (100-200x improvement)
- ✅ Reversible steganography support (Histogram Shift)
- ✅ Elegant Strategy Pattern design
Educational Value
- ✅ Interactive algorithm explanation panel
- ✅ Real-time logging system for operation tracking
- ✅ Histogram visualization display
- ✅ 4 screenshots demonstrating complete workflow
Engineering Practices
- ✅ MVP architecture separating UI and logic
- ✅ Dual-project solution (Class Library + Application)
- ✅ Complete error handling mechanism
- ✅ Progress indicator enhancing user experience
Learning Outcomes
- ✅ Deep implementation of information hiding techniques
- ✅ Mastered bitwise operations and pointer manipulation
- ✅ Understood practical application of design patterns
- ✅ Learned complex WinForms UI development
Application Screenshots